Multi-condition compound closed cooling tower
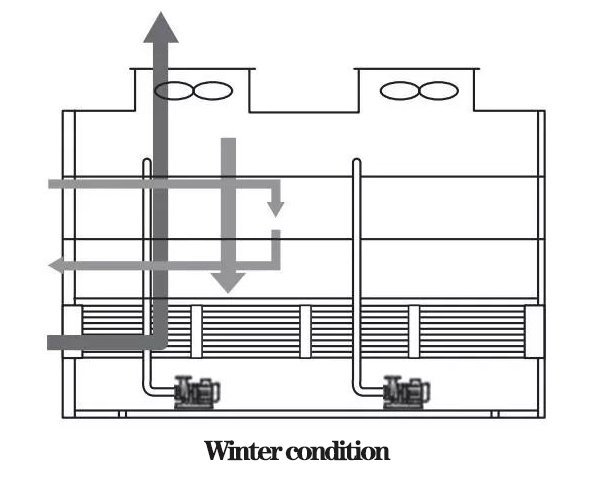
The multi-condition compound closed cooling tower is a cooling equipment with an open cooling system added on the basis of the traditional closed tower. The coil and the packing adopt different circuits, which have the high efficiency of water cooling of the packing and the high air volume characteristics of air cooling. It stops supplying water to the packing in late autumn to effectively avoid the packing being frozen. A four-stage operation strategy is designed according to the climate characteristics of extremely hot summer and extremely cold winter in North China and Northeast China.
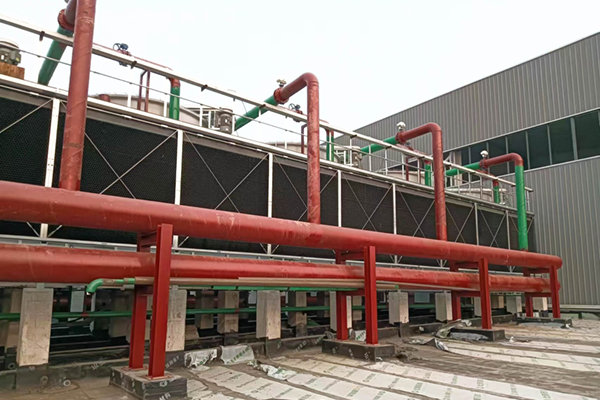

Physical picture of multi-condition compound closed cooling tower
1) Summer: open the closed and open cycle at the same time, the cold water produced by the open cycle is supplied to the closed cycle to meet the demand of extremely high heat load;
2) Early autumn: closed tower does not turn on, open tower is fully open, compared with summer mode power saving;
3) Late autumn: closed tower fully open, open tower fully closed, can prevent packing ice and tube row freezing at low temperature;
4) Winter: closed tower spray water off, only open the fan, open tower completely closed, conducive to energy saving and water saving.
Closed type mixed cooling tower
The closed hybrid cooling tower is equipped with a finned tube in series with the condensate coil, which has three operation modes, namely dry/wet combined mode, adiabatic mode and dry mode. Through the selection of different operation modes, it can be applied to areas requiring continuous and reliable operation, high water price, and occasions where water supply is limited or white fog needs to be eliminated.
Closed type mixed cooling tower
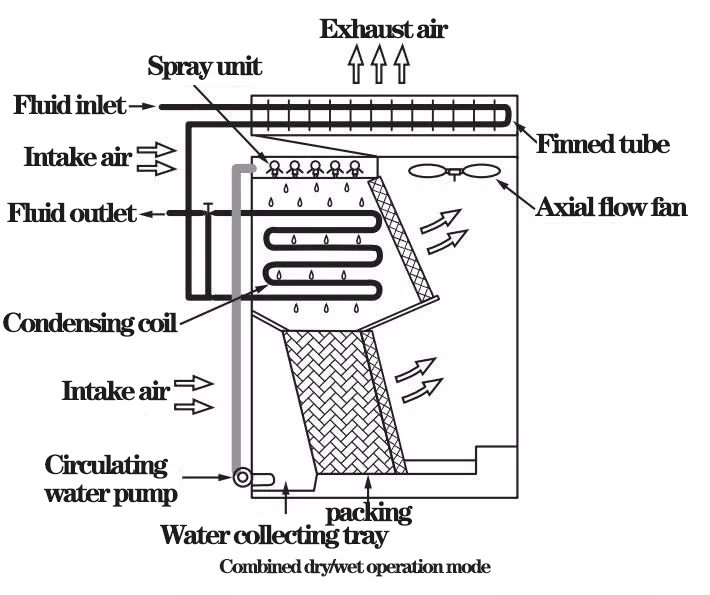
1) Dry/wet combined operation mode
The fluid first enters the finned tube for cooling and then enters the condensate coil for further cooling. The spray water is sent from the collecting pan by the circulating pump to the spray unit above the condensate coil. The spray water wets the surface of the condensate coil, takes away the heat of the fluid in the tube and falls to the surface of the packing, which is further cooled in the packing and then falls into the water collecting pan for recycling. The air flows through the packing and condensing coil respectively, absorbing heat to reach saturation state and then discharged by axial flow fan. At this time, the exhaust temperature is relatively low, and the fluid in the finned tube installed above the axial flow fan can be cooled significantly by the exhaust air.
The combined dry/wet operation mode utilizes sensible heat and latent heat of evaporation. Compared with traditional cooling towers, the tendency of white fog is greatly reduced in extreme weather, and a lot of water can be saved.
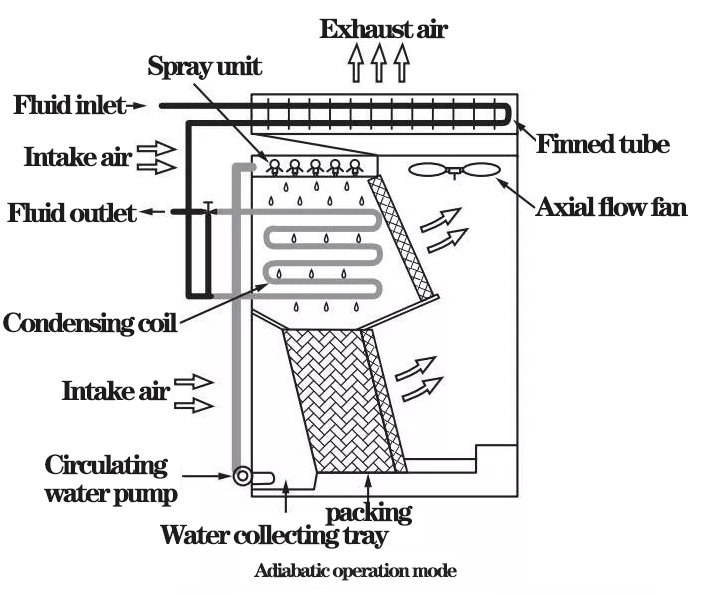
2) adiabatic operation mode
In adiabatic operation mode, all the fluid cooled by the finned tube is discharged by bypass. There is no heat exchange in the condensate coil, and the spray water is only used to pre-cool the air entering from the outside. Under most climate conditions, the surrounding air still has considerable potential to absorb water, the temperature of the adiabatic cooling air is significantly reduced, and the fluid inside the finned tube is pre-cooled when discharged by the axial flow fan to ensure the temperature required by the design fluid, so as to maximize the system efficiency.
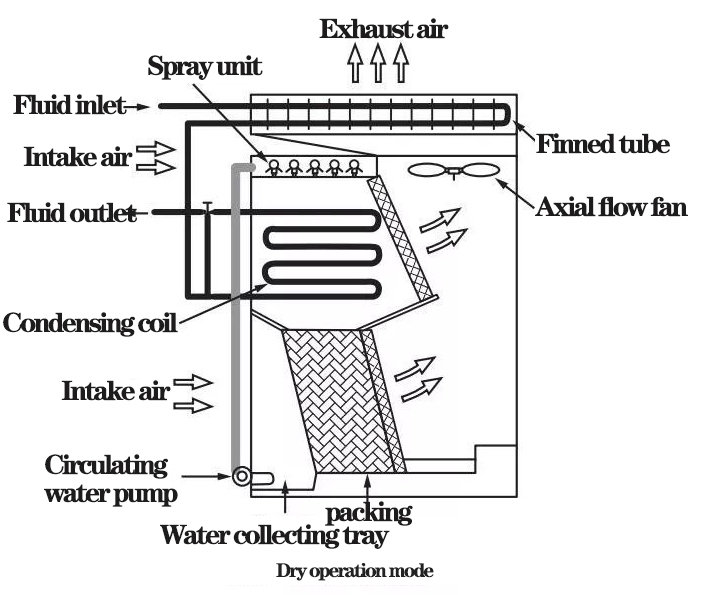
3) Dry operation mode
In dry operation mode, the spray water system is closed, saving pump energy consumption. The fluid to be cooled flows through the finned tube into the condensate coil. The flow control valve is kept fully open to ensure that the fluid flows through the two coils in series to maximize the heat transfer area. In this model, no water is consumed by evaporation and no white fog is produced at all. When the dry operation mode lasts for a long time, the water in the collecting pan is emptied, so that the problem of anti-freezing and water treatment is not needed to be considered.
Closed type mixed cooling tower operation mode
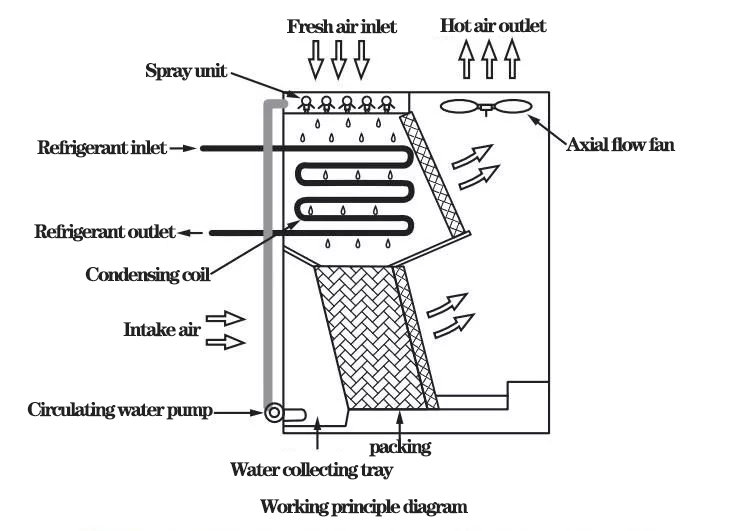
Evaporative condenser
Packing evaporative condenser
Physical diagram and working principle diagram of packed evaporative condenser. Gaseous refrigerant enters coil and transfers heat through coil surface to fin. The outdoor air is sucked into the unit by a fan located at the top, and cooled by constant enthalpy as it passes through a wet filler located on one side of the coil. After that, the precooled air flowing over the coil and fin surface carries away the heat of the refrigerant in the tube, condensing it into liquid refrigerant.
Packing type evaporative condenser physical diagram and working principle diagram
Drench evaporative condenser
The water-eluted evaporative condenser mainly relies on water evaporating in the air to take away the heat of the gaseous refrigerant in the pipe and condense it into liquid refrigerant. According to the direction of air flow and spray water, it can be divided into down-flow evaporative condenser and counter-flow evaporative condenser.
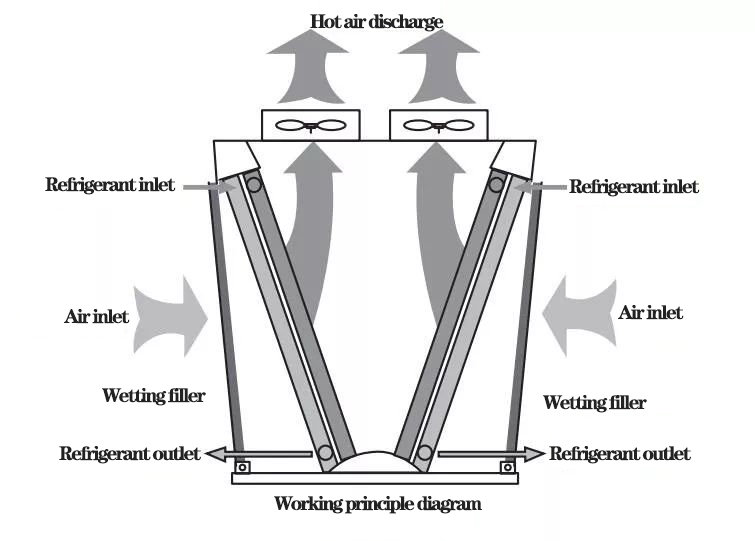
Down-flow evaporative condenser
Down-flow evaporative condenser (because part of the air enters from above the coil, in the same direction as the spray water, so it is called down-flow condenser) is provided with a spray device, condensing coil, packing, water collection plate, etc. A circulating water pump is arranged outside the box body, and an axial flow fan is arranged at the top of the side of the condensate coil. During operation, the cooling water is sent to the spray device above the condensate coil by the circulating water pump, and sprayed uniformly on the outer surface of the condensate coil to form a very thin layer of water film. Through the ventilation of the axial flow fan, the air enters the equipment from the top of the coil and the side of the packing, strengthens the air flow, forms the negative pressure in the box, reduces the evaporation temperature of water, promotes the evaporation of water film, and strengthens the heat release of the condensing coil. High temperature gaseous refrigerant enters from the upper part of the condensate coil, becomes liquid refrigerant after being condensed by the water film outside the tube, and flows out from the lower collector of the condensate coil. After the water film absorbs the heat of the refrigerant, part of it evaporates into water vapor which is sucked away and discharged into the atmosphere by the axial flow fan. The other parts exchange heat and humidity with the air after the packing, and then fall into the water collection tray for recycling.
Physical diagram and working principle diagram of down-flow evaporative condenser
Countercurrent evaporative condenser
When the countercurrent evaporative condenser (air and spray water in the opposite direction, called countercurrent) runs, the cooling water is sent to the spray device by the circulating water pump, and uniform water film is formed on the surface of the heat exchange coil. Outdoor air enters the equipment from the lower part, and heat and humidity exchange occurs with the water film, promoting the evaporation rate of the water film, taking away the heat of the refrigerant in the heat exchange coil, and condensing the gaseous refrigerant into liquid outflow.
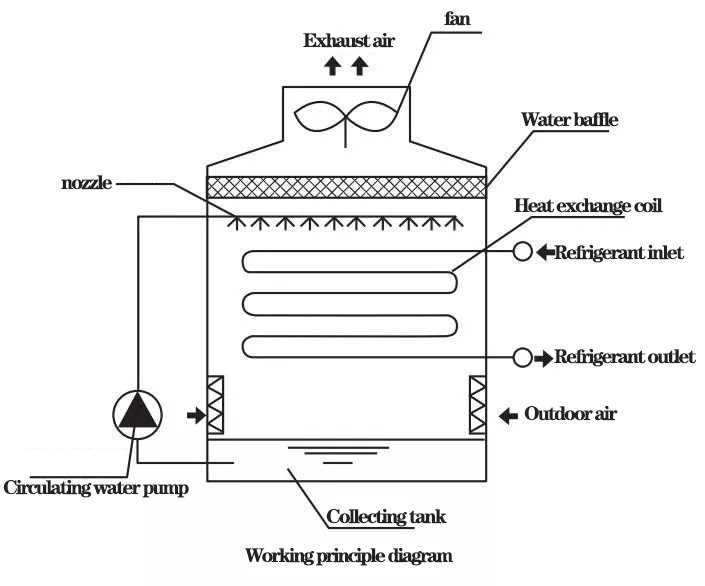
Countercurrent evaporative condenser physical diagram and working principle diagram
Evaporative condensation chiller/air conditioning unit
Evaporation-cooled maglev unit
Evaporative cooling maglev unit, the unit adopts falling film evaporator, water evaporative condenser and innovative control logic, to achieve unit integration design.
Figure 7 Evaporative cooling maglev unit/air conditioning unit
After entering the falling film evaporator, the refrigerant drops evenly to the outside of the evaporation heat exchange tube through the nozzle of the dispenser. The refrigerant flows down the outer surface of the heat exchange tube in a film shape, endothermic vaporization on the outside of the heat exchange tube, and carries out heat exchange with the fluid in the heat exchange tube along the surrounding of the heat exchange tube. The gaseous refrigerant formed moves from the bottom up from the gap of the heat exchange tube. Exit the evaporator through the steam outlet of the evaporator.
The water-eluting evaporative condenser is highly integrated with the condenser and cooling tower. With air and water as the cooling medium, the latent heat of vaporization of water is used to take away the condensation heat of refrigerant and realize the condensation of refrigerant vapor. Therefore, the demand for water is greatly reduced and the water can save 55% of water.
Evaporation-condensing chiller
Evaporation-condensing chiller. Evaporation-condensing chiller is a kind of air conditioning equipment with high energy efficiency, which has been applied in subway air conditioning system at present. Because it avoids the setting problem of cooling tower, the layout is more flexible, and the system energy consumption is reduced while meeting the temperature and humidity requirements, which has practical significance for the energy saving of subway ventilation and air conditioning system.
Evaporation-condensing chiller
Physical picture of plate and tube evaporative condensation chiller. Plate and tube evaporative condensation chiller adopts flat liquid film heat transfer technology, uniform water distribution, high heat transfer efficiency. When working, the compressor inhales the high temperature and low pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator, increases the pressure and sends it to the evaporative condenser. Under the combined action of circulating water outside the tube and outdoor air, the refrigerant liquid is cooled into low temperature and high pressure. After entering the throttling device, the refrigerant liquid becomes low temperature and low pressure and sends it into the evaporator to evaporate and absorb heat and cool the high temperature frozen water. Into high temperature and low pressure refrigerant vapor, and then into the compressor, complete a cycle.
Plate and tube evaporative condensation chiller
Concluding remarks
The exhibition of evaporative cooling equipment promoted the technical exchange of evaporative cooling and related industries, and played a positive role in discussing the new progress of evaporative cooling and refrigeration technology and spreading the concept of green and energy-saving design.
The development of evaporative cooling technology is closely related to the development of air conditioning technology. From the birth of the first air conditioner in the world to the natural cooling of data centers, to evaporative air conditioners and evaporative cooling fans, evaporative cooling air conditioners have been widely used in subway stations, airports, data centers and other related fields. It plays an increasingly important role in ventilation and air conditioning of industrial and civil buildings.
With the Belt and Road Initiative, evaporative cooling technology faces new opportunities and challenges. Evaporative cooling, an energy-saving, environmentally friendly, economic and healthy cooling method, is highly compatible with the economic and energy conditions of countries along the Belt and Road, especially Kazakhstan, Iran, Saudi Arabia and other regions with dry climate and abundant dry air. Researchers should have a deeper understanding of the climate characteristics and energy forms of countries and regions along the Belt and Road, and use evaporative cooling air conditioning technology according to local conditions. It is believed that in the near future, evaporative cooling technology will become the leading way of air conditioning in countries and regions along the Belt and Road, and become the future of air conditioning in these regions, making due contributions to environmental protection, energy saving and emission reduction.
Post time: Jun-12-2023

